Who Owns The United States Of America Today

The question of who owns the United States of America today is complex and multifaceted, involving various entities and interests. To understand this, it's essential to delve into the country's history, its economic structure, and the nature of its government. The United States is a federal republic with a democratic system, where the ownership and control of assets, resources, and institutions are distributed among different sectors, including the public sector, private corporations, and individual citizens.
Historical Context and Constitutional Framework
The United States was founded on principles of liberty, democracy, and private property, as enshrined in its Constitution and the Bill of Rights. The concept of ownership in the U.S. is deeply rooted in these documents, which establish the rights of individuals to own property and engage in economic activities. Historically, the country’s development has been shaped by the interplay between government policies, economic growth, and the influence of various interest groups.
Economic Structure and Ownership
The U.S. economy is characterized by a mix of public and private ownership. The government owns and operates certain key sectors, such as defense, infrastructure, and some public services. However, the majority of the economy is driven by private enterprise, with corporations, small businesses, and individual entrepreneurs playing a significant role. The distribution of wealth and ownership is a critical aspect of the U.S. economy, with a significant portion of the country’s wealth concentrated among a small percentage of the population.
| Category | Percentage of Wealth Ownership |
|---|---|
| Top 1% of the Population | Approximately 40% |
| Next 9% of the Population | Approximately 27% |
| Bottom 90% of the Population | Approximately 33% |

Foreign Ownership and Influence

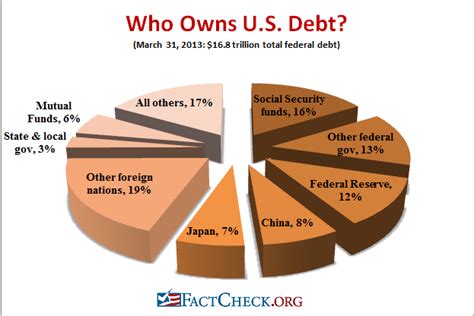
In addition to domestic ownership, foreign entities also hold significant interests in the U.S. economy. Foreign investment in the United States takes many forms, including direct investment in businesses, real estate, and the purchase of U.S. government securities. As of the latest available data, foreign governments and private investors hold a substantial portion of the U.S. national debt, with countries like China and Japan being among the largest holders.
Government Debt and Foreign Ownership
The issue of foreign ownership of U.S. government debt is a topic of ongoing debate. While it reflects the global nature of financial markets and the attractiveness of U.S. securities, it also raises questions about the implications for national sovereignty and economic policy. The dependency on foreign capital to finance government spending can influence monetary and fiscal policies, affecting the overall direction of the U.S. economy.
Key Points
- The ownership of the United States is complex, involving public, private, and foreign entities.
- The concentration of wealth among a small percentage of the population is a significant factor in the country's economic landscape.
- Foreign investment and ownership, including the holding of U.S. government debt, play a crucial role in the U.S. economy.
- The distribution of ownership and wealth has implications for economic policies, national sovereignty, and the direction of the country's development.
- Understanding the nuances of ownership in the U.S. requires a comprehensive analysis of historical, economic, and political factors.
In conclusion, the question of who owns the United States of America today does not have a simple answer. The country's ownership structure is a dynamic and complex system, influenced by a multitude of domestic and foreign factors. As the global economy continues to evolve, the nature of ownership and control in the United States will likely undergo further changes, reflecting shifting economic realities, political priorities, and societal values.
What are the implications of foreign ownership of U.S. government debt?
+The implications of foreign ownership of U.S. government debt are multifaceted. It can influence the country’s monetary and fiscal policies, affect the value of the dollar, and have broader implications for the U.S. economy and national sovereignty.
How does the concentration of wealth among a small percentage of the population affect the U.S. economy?
+The concentration of wealth can lead to reduced economic mobility, increased income inequality, and decreased economic growth. It can also influence political policies and decision-making, further exacerbating economic disparities.
What role does the government play in shaping the ownership structure of the United States?
+The government plays a significant role in shaping the ownership structure through policies, regulations, and tax laws. These measures can encourage or discourage certain types of investment, influence the distribution of wealth, and impact the overall economic landscape.



