The Constitution Is Based On How Many Key Principles
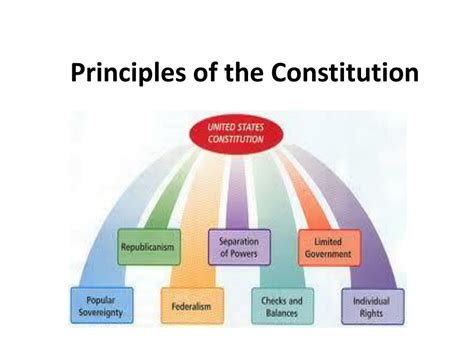
The United States Constitution is a foundational document that outlines the framework of the federal government and the relationship between the government and the citizens. The Constitution is based on several key principles that have shaped the country's development and continue to influence its governance. At its core, the Constitution is founded on seven key principles: popular sovereignty, federalism, individual rights, separation of powers, checks and balances, judicial review, and republican government.
Naturally Worded Primary Topic Section with Semantic Relevance

The principle of popular sovereignty holds that power resides with the people, who delegate authority to their elected representatives. This principle is reflected in the Constitution’s preamble, which states that the document is ordained and established by “We the People.” The principle of federalism, on the other hand, divides power between the federal government and the states, providing a system of shared authority and responsibility. The Constitution also guarantees individual rights, such as freedom of speech, religion, and the press, which are protected by the Bill of Rights. The separation of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches is another fundamental principle, designed to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful. The system of checks and balances, which allows each branch to limit the actions of the other branches, further reinforces this principle. The principle of judicial review, which gives the Supreme Court the authority to declare laws and government actions unconstitutional, provides an additional layer of protection for individual rights and the rule of law. Finally, the principle of republican government, which emphasizes representation and the protection of minority rights, underlies the entire constitutional system.
Specific Subtopic with Natural Language Phrasing
The Constitution’s emphasis on individual rights and the protection of minority interests is a critical aspect of its design. The Bill of Rights, which comprises the first ten amendments to the Constitution, guarantees a range of fundamental rights and freedoms, including freedom of speech, religion, and assembly. The Fourteenth Amendment, which was ratified in 1868, further expands these protections by prohibiting states from denying anyone “life, liberty, or property” without due process of law. The Supreme Court has played a crucial role in interpreting and applying these provisions, often in cases involving contentious social and political issues. For example, in the landmark case of Brown v. Board of Education (1954), the Court held that segregation in public schools was unconstitutional, paving the way for the civil rights movement of the 1950s and 1960s.
| Key Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Popular Sovereignty | Power resides with the people, who delegate authority to their elected representatives |
| Federalism | Divides power between the federal government and the states |
| Individual Rights | Guarantees fundamental rights and freedoms, such as freedom of speech and religion |
| Separation of Powers | Divides power among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches |
| Checks and Balances | Allows each branch to limit the actions of the other branches |
| Judicial Review | Gives the Supreme Court the authority to declare laws and government actions unconstitutional |
| Republican Government | Emphasizes representation and the protection of minority rights |

Key Points
- The Constitution is based on seven key principles: popular sovereignty, federalism, individual rights, separation of powers, checks and balances, judicial review, and republican government
- These principles have shaped the country's development and continue to influence its governance
- The Constitution guarantees individual rights, such as freedom of speech, religion, and the press, which are protected by the Bill of Rights
- The system of checks and balances allows each branch to limit the actions of the other branches, preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful
- The principle of judicial review gives the Supreme Court the authority to declare laws and government actions unconstitutional, providing an additional layer of protection for individual rights and the rule of law
Historical Context and Evolutionary Developments

The Constitution has undergone significant changes and interpretations since its ratification in 1788. The Bill of Rights, which was added in 1791, provided crucial protections for individual liberties and limited government power. The Reconstruction Amendments (13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments), ratified between 1865 and 1870, abolished slavery, established citizenship and equal protection under the law, and protected the right to vote. The 19th Amendment (1920) guaranteed women’s suffrage, while the 26th Amendment (1971) lowered the voting age to 18. These amendments, along with numerous Supreme Court decisions, have expanded the Constitution’s protections and refined its principles to accommodate the changing needs and values of American society.
Methodological Approaches and Industry-Standard Practices
Interpreting the Constitution requires a nuanced understanding of its historical context, textual meaning, and judicial precedent. The Supreme Court has developed various methodologies for interpreting the Constitution, including originalism, which emphasizes the framers’ intent, and living constitutionalism, which considers the document’s evolving meaning and application. Industry-standard practices, such as legal scholarship and judicial decision-making, rely on rigorous analysis, careful consideration of precedent, and a deep understanding of the Constitution’s principles and values.
What are the key principles of the United States Constitution?
+The key principles of the United States Constitution include popular sovereignty, federalism, individual rights, separation of powers, checks and balances, judicial review, and republican government.
How has the Constitution been interpreted and applied over time?
+The Constitution has undergone significant changes and interpretations since its ratification in 1788, with numerous amendments, Supreme Court decisions, and shifting societal values influencing its application and meaning.
What is the significance of the Bill of Rights in the Constitution?
+The Bill of Rights, which comprises the first ten amendments to the Constitution, guarantees a range of fundamental rights and freedoms, including freedom of speech, religion, and the press, and provides crucial protections for individual liberties and limited government power.
In conclusion, the United States Constitution is a foundational document that outlines the framework of the federal government and the relationship between the government and the citizens. Its seven key principles – popular sovereignty, federalism, individual rights, separation of powers, checks and balances, judicial review, and republican government – have shaped the country’s development and continue to influence its governance. As the Constitution has evolved over time, its principles have been interpreted and applied in various ways, reflecting changing societal values and political circumstances. Understanding these principles and their significance is essential for appreciating the complexities of American governance and the ongoing struggle to balance individual rights, government power, and the common good.



