Texas Constitution Vs U.s. Constitution
The Texas Constitution and the United States Constitution are two foundational documents that shape the governance and laws of their respective jurisdictions. While both documents share some similarities, they also have distinct differences in terms of their history, structure, and content. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of both constitutions, exploring their unique features, and examining the interplay between them.
Historical Context and Development

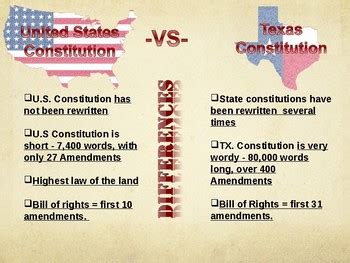
The United States Constitution, adopted on September 17, 1787, is the supreme law of the land, outlining the framework of the federal government and the relationship between the government and the citizens. The Texas Constitution, on the other hand, has undergone several revisions since its first adoption in 1827, with the current version being ratified in 1876. The Texas Constitution has been amended numerous times, with over 490 amendments to date, making it one of the longest state constitutions in the United States.
Structure and Organization
The United States Constitution is divided into seven Articles, with a preamble and a list of amendments. The Texas Constitution, in contrast, is divided into 17 Articles, with a preamble and a list of amendments. While both documents establish the basic principles of governance, the Texas Constitution provides more detailed provisions on various aspects of state governance, such as education, local government, and taxation.
| Constitutional Provisions | U.S. Constitution | Texas Constitution |
|---|---|---|
| Bill of Rights | 1st-10th Amendments | Article I, Sections 1-31 |
| Legislative Branch | Article I, Sections 1-10 | Article III, Sections 1-49 |
| Executive Branch | Article II, Sections 1-4 | Article IV, Sections 1-22 |
| Judicial Branch | Article III, Sections 1-3 | Article V, Sections 1-31 |

Key Differences and Similarities

One of the primary differences between the two constitutions is the scope of their authority. The United States Constitution sets forth the framework for the federal government, while the Texas Constitution governs the state government and its relationships with local governments and citizens. Both documents, however, establish the principles of federalism, ensuring that power is divided between the national and state governments.
Bill of Rights and Individual Liberties
Both constitutions contain provisions protecting individual liberties and rights, such as freedom of speech, assembly, and due process. The Texas Constitution, however, provides more explicit protections for certain rights, such as the right to bear arms and the right to a fair trial. The United States Constitution, on the other hand, has been interpreted by the courts to provide broader protections for individual rights, such as the right to privacy and the right to equal protection under the law.
Key Points
- The Texas Constitution has undergone numerous amendments, resulting in a more detailed and lengthy document compared to the U.S. Constitution.
- Both constitutions establish the principles of federalism, dividing power between the national and state governments.
- The Texas Constitution provides more explicit protections for certain individual rights, such as the right to bear arms and the right to a fair trial.
- The U.S. Constitution has been interpreted by the courts to provide broader protections for individual rights, such as the right to privacy and the right to equal protection under the law.
- The interplay between the two constitutions is complex, with the U.S. Constitution setting the framework for federal authority and the Texas Constitution governing state governance and individual rights.
Interplay and Conflict Between the Two Constitutions
The relationship between the Texas Constitution and the United States Constitution is complex, with both documents influencing the governance and laws of the state. The U.S. Constitution sets the framework for federal authority, while the Texas Constitution governs state governance and individual rights. In cases where the two constitutions conflict, the U.S. Constitution takes precedence, as established by the Supremacy Clause (Article VI, Clause 2). However, the Texas Constitution can provide additional protections for individual rights and liberties, as long as they do not conflict with federal law.
Implications for Governance and Policy
The interplay between the two constitutions has significant implications for governance and policy in Texas. The state’s unique constitutional provisions, such as the emphasis on individual rights and local control, can shape the development of state laws and policies. Additionally, the U.S. Constitution’s broader protections for individual rights can influence the interpretation and application of Texas laws, particularly in areas such as civil rights and social justice.
What is the main difference between the Texas Constitution and the U.S. Constitution?
+The main difference between the two constitutions is the scope of their authority, with the U.S. Constitution setting the framework for the federal government and the Texas Constitution governing the state government and its relationships with local governments and citizens.
How do the two constitutions protect individual liberties and rights?
+Both constitutions contain provisions protecting individual liberties and rights, such as freedom of speech, assembly, and due process. However, the Texas Constitution provides more explicit protections for certain rights, such as the right to bear arms and the right to a fair trial, while the U.S. Constitution has been interpreted by the courts to provide broader protections for individual rights.
What happens in cases where the two constitutions conflict?
+In cases where the two constitutions conflict, the U.S. Constitution takes precedence, as established by the Supremacy Clause (Article VI, Clause 2). However, the Texas Constitution can provide additional protections for individual rights and liberties, as long as they do not conflict with federal law.
In conclusion, the Texas Constitution and the United States Constitution are two distinct documents with unique features and provisions. While both constitutions establish the principles of federalism and protect individual liberties and rights, they differ in their scope, structure, and content. Understanding the interplay between these two constitutions is essential for navigating the complex landscape of governance and policy in Texas, and for appreciating the state’s unique cultural and historical identity.



