Mountain Ranges In The United States

The United States is home to some of the most spectacular and diverse mountain ranges in the world. From the rugged peaks of the Rocky Mountains to the ancient Appalachian Mountains, each range has its own unique character and attractions. The mountain ranges in the United States are not only breathtakingly beautiful, but they also play a crucial role in shaping the country's climate, geology, and ecosystem. In this article, we will explore the major mountain ranges in the United States, their geography, geology, and the impact they have on the environment and human activities.
Key Points
- The Rocky Mountains are the longest mountain range in the United States, stretching over 3,000 miles from British Columbia, Canada, to New Mexico.
- The Appalachian Mountains are the oldest mountain range in the United States, with rocks dating back over 480 million years.
- The Sierra Nevada mountain range is home to some of the highest peaks in the contiguous United States, including Mount Whitney, the highest peak in the lower 48 states.
- The Cascade Range is known for its volcanic activity, with mountains like Mount St. Helens and Mount Rainier being prominent examples.
- The Ozark Mountains are a unique and diverse range, with a mix of rugged terrain, scenic valleys, and abundant wildlife.
The Rocky Mountains

The Rocky Mountains are one of the most iconic and awe-inspiring mountain ranges in the United States. Stretching over 3,000 miles from British Columbia, Canada, to New Mexico, the Rockies are the longest mountain range in the country. The range is divided into several sub-ranges, including the Colorado Rockies, the Wyoming Rockies, and the Montana Rockies. The Rockies are known for their rugged peaks, alpine lakes, and abundant wildlife, including grizzly bears, mountain goats, and bighorn sheep. The highest peak in the Rocky Mountains is Mount Elbert, located in Colorado, which stands at an elevation of 14,433 feet.
Geology of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains were formed over 70 million years ago during the Laramide orogeny, a period of mountain building that occurred when the North American plate collided with the Pacific plate. The range is composed of a variety of rocks, including granite, gneiss, and shale, which were uplifted and folded during the collision. The Rockies are also home to numerous faults, including the Rocky Mountain Fault, which runs along the eastern edge of the range. The geology of the Rockies has played a significant role in shaping the range’s landscape, with erosion and weathering creating a diverse range of landforms, including canyons, valleys, and peaks.
| Mountain Range | Length (miles) | Height (feet) |
|---|---|---|
| Rocky Mountains | 3,000 | 14,433 |
| Appalachian Mountains | 2,400 | 6,684 |
| Sierra Nevada | 400 | 14,505 |
| Cascade Range | 700 | 14,411 |
| Ozark Mountains | 500 | 2,600 |
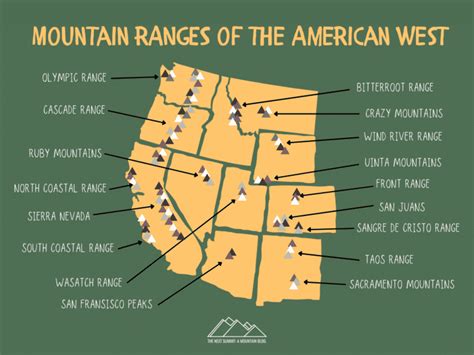
The Appalachian Mountains

The Appalachian Mountains are the oldest mountain range in the United States, with rocks dating back over 480 million years. The range stretches from Quebec, Canada, to Alabama, covering a distance of over 2,400 miles. The Appalachians are a relatively low-lying range, with the highest peak, Mount Mitchell, standing at an elevation of 6,684 feet. The range is known for its rolling hills, scenic valleys, and abundant coal deposits. The Appalachians have a rich cultural heritage, with numerous historic sites, including the Appalachian Trail, which stretches over 2,000 miles from Georgia to Maine.
Ecology of the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains are home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including deciduous forests, grasslands, and wetlands. The range is also home to numerous endangered species, including the eastern box turtle, the wood turtle, and the black bear. The Appalachians are also an important habitat for migratory birds, including the warbler, the thrush, and the sparrow. The range’s unique geology and climate have created a variety of microclimates, which support a wide range of plant and animal life.
The Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada mountain range is located in the western United States, stretching over 400 miles from California to Nevada. The range is known for its rugged terrain, scenic valleys, and abundant granite peaks. The highest peak in the Sierra Nevada is Mount Whitney, which stands at an elevation of 14,505 feet, making it the highest peak in the contiguous United States. The range is also home to numerous iconic landmarks, including Yosemite National Park, Lake Tahoe, and the John Muir Trail.
Geology of the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada was formed over 150 million years ago during the Jurassic period, when the North American plate collided with the Pacific plate. The range is composed of a variety of rocks, including granite, basalt, and sandstone, which were uplifted and folded during the collision. The Sierra Nevada is also home to numerous faults, including the San Andreas Fault, which runs along the western edge of the range. The geology of the Sierra Nevada has played a significant role in shaping the range’s landscape, with erosion and weathering creating a diverse range of landforms, including canyons, valleys, and peaks.
The Cascade Range
The Cascade Range is a chain of mountains located in the Pacific Northwest, stretching over 700 miles from British Columbia, Canada, to Northern California. The range is known for its volcanic activity, with mountains like Mount St. Helens and Mount Rainier being prominent examples. The highest peak in the Cascade Range is Mount Rainier, which stands at an elevation of 14,411 feet. The range is also home to numerous iconic landmarks, including Crater Lake National Park, Mount Baker, and the Columbia River Gorge.
Volcanic Activity in the Cascade Range
The Cascade Range is home to numerous active and dormant volcanoes, including Mount St. Helens, which erupted in 1980, causing widespread destruction and loss of life. The range is also home to numerous volcanic fields, including the Oregon Cascades and the Washington Cascades. The volcanic activity in the Cascade Range has created a unique landscape, with numerous volcanic peaks, lava flows, and ash deposits. The range’s volcanic activity has also played a significant role in shaping the region’s ecosystem, with numerous plant and animal species adapting to the unique conditions created by the volcanoes.
The Ozark Mountains

The Ozark Mountains are a unique and diverse range, located in the central United States, stretching over 500 miles from Missouri to Arkansas. The range is known for its rugged terrain, scenic valleys, and abundant wildlife. The highest peak in the Ozark Mountains is Taum Sauk Mountain, which stands at an elevation of 1,772 feet. The range is also home to numerous iconic landmarks, including Mark Twain National Forest, Ozark National Scenic Riverways, and the Buffalo National River.
Ecology of the Ozark Mountains
The Ozark Mountains are home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including deciduous forests, grasslands, and wetlands. The range is also home to numerous endangered species, including the Ozark hellbender, the eastern box turtle, and the black bear. The Ozarks are also an important habitat for migratory birds, including the warbler, the thrush, and the sparrow. The range’s unique geology and climate have created a variety of microclimates, which support a wide range of plant and animal life.
What is the longest mountain range in the United States?
+The Rocky Mountains are the longest mountain range in the United States, stretching over 3,000 miles from British Columbia, Canada, to New Mexico.
What is the highest peak in the contiguous United States?
+Mount Whitney, located in the Sierra Nevada mountain range, is the highest peak in the contiguous United States, standing at an elevation of 14,505 feet.
What is the oldest mountain range in the United States?
+The Appalachian Mountains are the oldest mountain range in the United States, with rocks dating back over 480 million years.
Meta Description: Discover the majestic mountain ranges in the United States, including the Rocky Mountains, Appalachian Mountains, Sierra Nevada, Cascade Range, and Ozark Mountains. Learn about their geography, geology, and ecosystem, and explore the unique attractions and landmarks of each range.



