Map Of Us And Islands
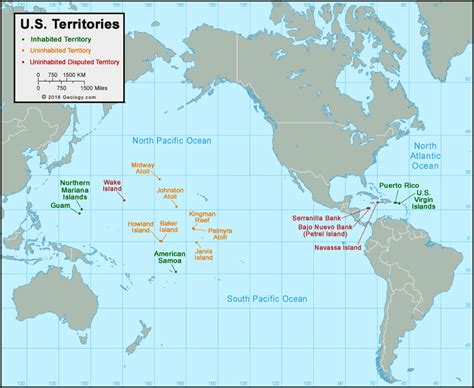
The United States of America is a vast and diverse country, comprising not only the continental landmass but also a multitude of islands that are scattered across the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. These islands, while geographically distinct, are integral parts of the country, offering unique cultural, ecological, and strategic values. Understanding the layout and significance of these islands is crucial for grasping the full extent of U.S. territory and its implications for national defense, environmental conservation, and economic development.
Key Points
- The United States encompasses a significant number of islands, both in the Pacific and the Caribbean, which are integral to its territorial claims and strategic interests.
- These islands are home to diverse ecosystems, including coral reefs, rainforests, and volcanic landscapes, contributing to global biodiversity.
- The economic importance of these islands ranges from tourism and fishing to the extraction of natural resources, such as oil and minerals.
- Strategically, the islands play a crucial role in military defense and international relations, with several hosting U.S. military bases.
- Environmental challenges, including climate change and conservation efforts, are critical issues for the sustainability of these island ecosystems and the communities that depend on them.
Introduction to U.S. Islands
The map of the U.S. and its islands reveals a complex geography that stretches far beyond the continental United States. From the state of Hawaii, an archipelago in the Pacific, to Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Guam in the Caribbean and Pacific, respectively, each island or island group has its own distinct history, culture, and ecological characteristics. The political status of these islands varies; some are states (like Hawaii), while others are territories or insular areas (such as Puerto Rico, Guam, the U.S. Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and the Northern Mariana Islands).
Pacific Islands
In the Pacific, the U.S. territory includes several significant island groups. Hawaii, the 50th state to join the Union, is renowned for its volcanic landscapes, beautiful beaches, and unique biodiversity. Other Pacific territories, such as Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands, are strategically important for U.S. military operations in the Asia-Pacific region. American Samoa, located southeast of Samoa, is another U.S. territory in the Pacific, known for its tropical rainforests and coral reefs.
| Island/Territory | Location | Political Status |
|---|---|---|
| Hawaii | Pacific Ocean | State |
| Guam | Pacific Ocean | Unincorporated Territory |
| Northern Mariana Islands | Pacific Ocean | Commonwealth |
| American Samoa | Pacific Ocean | Unincorporated Territory |
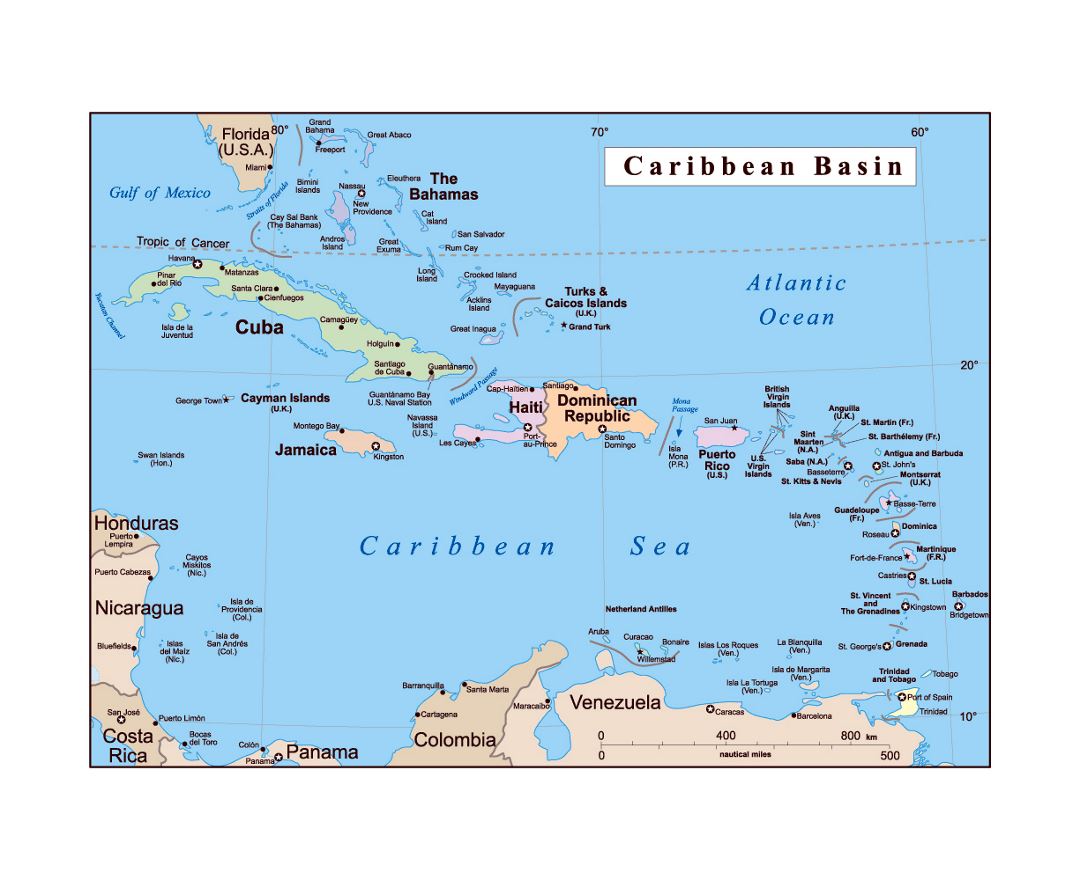
Caribbean Islands

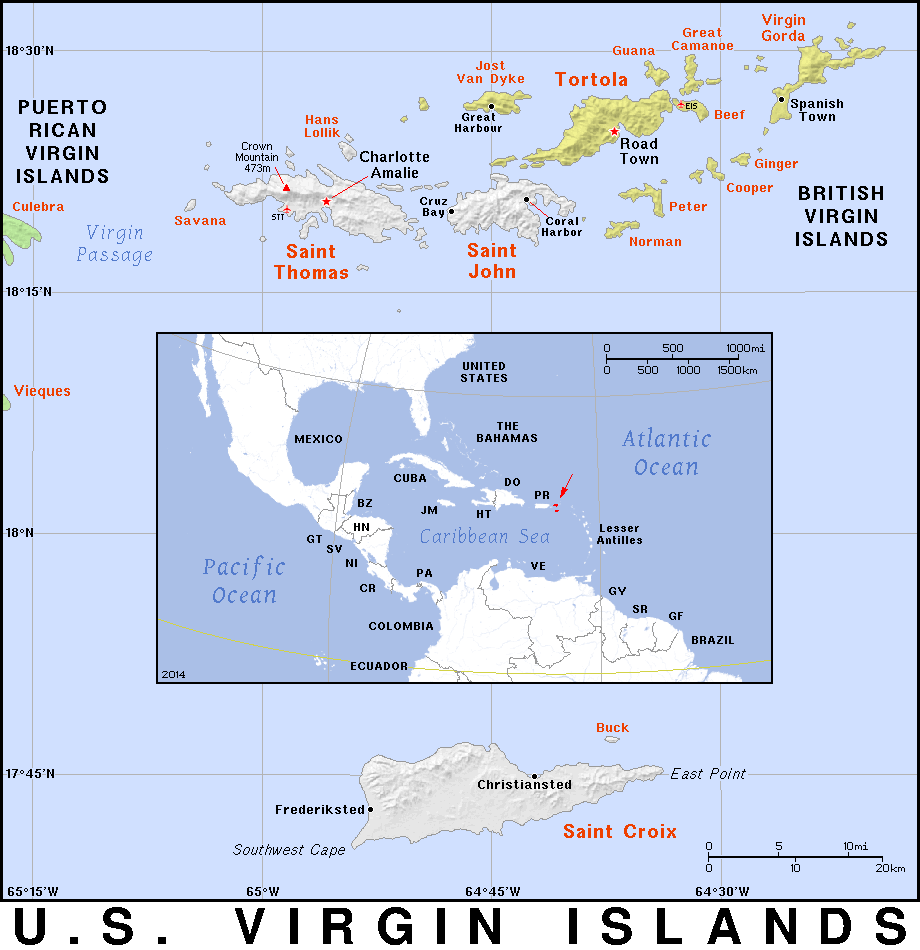
In the Caribbean, the U.S. has several territories, each with its unique culture and history. Puerto Rico, with its Spanish colonial past, is the most populous U.S. territory and has been a point of discussion regarding its potential statehood. The U.S. Virgin Islands, purchased from Denmark in 1917, are known for their beautiful beaches and have become a popular tourist destination. These islands are not only important for their natural beauty and economic contribution through tourism but also for their strategic military locations.
Economic and Environmental Significance
Beyond their strategic and cultural significance, the U.S. islands are also crucial for their economic and environmental contributions. Tourism is a major industry for many of these islands, with visitors drawn to their natural beauty, including coral reefs, rainforests, and volcanic landscapes. However, this economic activity must be balanced with the need to protect these fragile ecosystems, which are facing significant threats from climate change, overfishing, and pollution.
Furthermore, the extraction of natural resources, such as oil and minerals, is another economic activity present in some of these territories. Yet, the exploitation of these resources raises environmental concerns and highlights the need for sustainable development practices that prioritize the long-term health of these ecosystems and the well-being of their inhabitants.
What is the strategic importance of U.S. islands in the Pacific and Caribbean?
+The U.S. islands in the Pacific and Caribbean are crucial for military defense and international relations, hosting several U.S. military bases that contribute to regional stability and security.
How do the U.S. islands contribute to global biodiversity?
+The U.S. islands are home to diverse ecosystems, including coral reefs, rainforests, and volcanic landscapes, which contribute significantly to global biodiversity and support a wide range of unique and endemic species.
What are the economic activities present in the U.S. islands?
+The primary economic activities in the U.S. islands include tourism, fishing, and the extraction of natural resources. However, these activities must be managed sustainably to protect the islands' fragile ecosystems and ensure long-term economic viability.
In conclusion, the map of the U.S. and its islands paints a picture of a country with a rich geographical diversity, strategic importance, and a complex array of cultural, economic, and environmental issues. As the world faces the challenges of climate change, global security, and sustainable development, the role and management of these U.S. islands will become increasingly critical. Balancing the needs of economic development, environmental protection, and strategic security will be essential for ensuring the long-term viability and prosperity of these unique and valuable territories.



