Longitude And Latitude Of United States
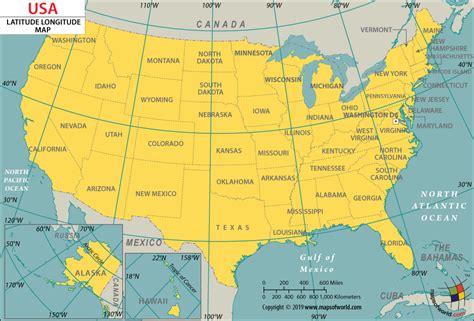
The United States, a vast and geographically diverse country, spans across a significant portion of North America. Understanding the longitude and latitude of the United States is crucial for navigation, geography, and various scientific applications. The country's unique shape, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and sharing international borders with Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, defines its geographical coordinates.
Geographical Extremes of the United States
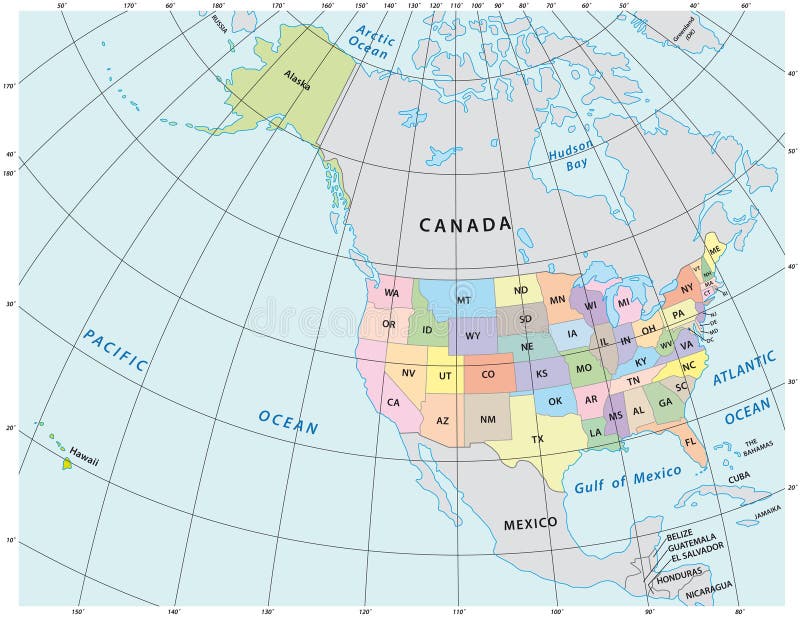
The United States covers a wide range of latitudes and longitudes, from the northernmost point in Point Barrow, Alaska, to the southernmost point in Key West, Florida. Similarly, the country’s easternmost and westernmost points are in West Quoddy Head, Maine, and Cape Dezhnev, Alaska, respectively. These geographical extremes play a significant role in determining the country’s overall longitude and latitude ranges.
Latitude Ranges
The latitude of the United States varies from approximately 24.396308° N in Key West, Florida, to 71.290556° N in Point Barrow, Alaska. This wide range of latitudes affects the climate, daylight hours, and overall geography of different regions within the country. For instance, the southern states experience a subtropical climate, while the northern states, especially Alaska, have a subarctic and arctic climate.
Longitude Ranges
The longitude of the United States ranges from approximately 66.934722° W in West Quoddy Head, Maine, to 124.733333° W in Cape Dezhnev, Alaska, and 124.844444° W in Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska. The variation in longitude influences the time zones across the country, with the easternmost states belonging to the Eastern Time Zone and the westernmost states belonging to the Pacific Time Zone.
| Location | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|
| Point Barrow, Alaska (Northernmost) | 71.290556° N | 156.768889° W |
| Key West, Florida (Southernmost) | 24.396308° N | 81.780056° W |
| West Quoddy Head, Maine (Easternmost) | 44.815278° N | 66.934722° W |
| Cape Dezhnev, Alaska (Westernmost) | 66.170556° N | 169.650556° W |

Key Points

Key Points
- The latitude of the United States ranges from approximately 24.396308° N to 71.290556° N.
- The longitude of the United States ranges from approximately 66.934722° W to 124.844444° W.
- The geographical extremes of the United States, including the northernmost, southernmost, easternmost, and westernmost points, define its overall longitude and latitude ranges.
- The variation in latitude and longitude affects the climate, daylight hours, and overall geography of different regions within the country.
- Understanding the geographical coordinates of the United States is crucial for navigation, geography, and various scientific applications.
Impact of Geographical Coordinates on Climate and Time Zones
The geographical coordinates of the United States have a significant impact on the climate and time zones across the country. The latitude, in particular, influences the amount of solar radiation received by different regions, resulting in varying climates. The longitude, on the other hand, affects the time zones, with the easternmost states experiencing earlier sunrise and sunset times compared to the westernmost states.
Climate Variations
The climate in the United States varies greatly from one region to another, with the northern states experiencing cold winters and mild summers, while the southern states have hot and humid summers and mild winters. The western states, including California and Arizona, have a Mediterranean climate, characterized by hot and dry summers and mild winters. Understanding the geographical coordinates of the United States is essential for predicting and preparing for extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and blizzards.
Time Zones
The United States spans across six time zones, including the Eastern Time Zone, Central Time Zone, Mountain Time Zone, Pacific Time Zone, Alaska Time Zone, and Hawaii-Aleutian Time Zone. The time zones are determined by the longitude, with each time zone representing a one-hour difference from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The variation in time zones affects the daily routines of people living in different regions, including work schedules, meal times, and sleep patterns.
What is the significance of understanding the geographical coordinates of the United States?
+Understanding the geographical coordinates of the United States is essential for navigation, geography, and various scientific applications. It helps predict and prepare for extreme weather events, determines the climate and time zones, and affects the overall geography of different regions.
How do the latitude and longitude of the United States affect the climate and time zones?
+The latitude and longitude of the United States affect the climate and time zones by influencing the amount of solar radiation received by different regions and determining the time zones based on the longitude. The latitude affects the climate, resulting in varying climates across the country, while the longitude affects the time zones, resulting in different sunrise and sunset times.
What are the geographical extremes of the United States?
+The geographical extremes of the United States include the northernmost point in Point Barrow, Alaska, the southernmost point in Key West, Florida, the easternmost point in West Quoddy Head, Maine, and the westernmost point in Cape Dezhnev, Alaska. These extremes define the overall longitude and latitude ranges of the country.
In conclusion, the longitude and latitude of the United States are essential geographical coordinates that affect the climate, time zones, and overall geography of different regions. Understanding these coordinates is crucial for navigation, geography, and various scientific applications. The geographical extremes of the United States, including the northernmost, southernmost, easternmost, and westernmost points, define the country’s overall longitude and latitude ranges. By recognizing the significance of these coordinates, we can better appreciate the complexity and diversity of the United States and its unique geographical characteristics.



