How Many Languages Are Spoken In The United States
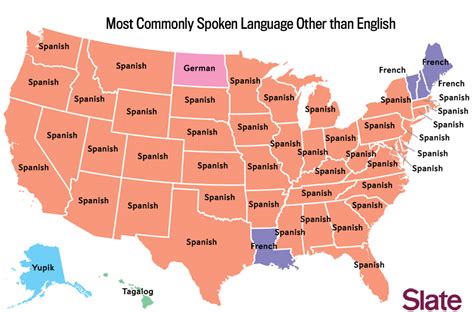
The United States is a melting pot of cultures, with a diverse population that speaks a wide range of languages. According to the United States Census Bureau, there are over 350 languages spoken in the country, making it one of the most linguistically diverse nations in the world. The majority of Americans speak English as their primary language, but there are also significant numbers of people who speak Spanish, Chinese, Tagalog, French, and many other languages.
Language diversity in the United States is not limited to immigrant communities. Many indigenous languages are also spoken in the country, including Navajo, Cherokee, and Inupiat. Additionally, there are several sign languages used by the deaf and hard of hearing community, including American Sign Language (ASL) and Signed Exact English (SEE).
The linguistic diversity of the United States is reflected in the country's language policies and practices. For example, the federal government provides language access services to limited English proficient (LEP) individuals, including interpretation and translation services. Many states and local governments also have their own language access policies and programs.
Key Points
- The United States is home to over 350 languages, making it one of the most linguistically diverse countries in the world.
- English is the primary language spoken by the majority of Americans, but there are also significant numbers of people who speak Spanish, Chinese, Tagalog, French, and many other languages.
- Indigenous languages, such as Navajo and Cherokee, are also spoken in the United States.
- Sign languages, including American Sign Language (ASL) and Signed Exact English (SEE), are used by the deaf and hard of hearing community.
- Language access services, including interpretation and translation, are provided to limited English proficient (LEP) individuals by the federal government and many states and local governments.
Language Demographics in the United States

According to the United States Census Bureau’s American Community Survey (ACS) 2019 estimates, the most spoken languages in the United States are:
| Language | Number of Speakers | Percentage of Population |
|---|---|---|
| English | 239 million | 82.3% |
| Spanish | 41 million | 14.2% |
| Chinese | 3.4 million | 1.2% |
| Tagalog | 1.7 million | 0.6% |
| French | 1.3 million | 0.5% |
| German | 1.1 million | 0.4% |
| Italian | 723,000 | 0.3% |
| Portuguese | 699,000 | 0.2% |
| Russian | 625,000 | 0.2% |
| Japanese | 477,000 | 0.2% |
| Korean | 423,000 | 0.1% |
| Arabic | 395,000 | 0.1% |
| Vietnamese | 341,000 | 0.1% |

Language Use and Language Shift
Language use and language shift are complex phenomena that involve the dynamic interaction of various factors, including demographics, education, economy, and culture. In the United States, language shift often occurs as immigrant communities become more assimilated into the dominant culture. For example, many second-generation immigrants may prefer to speak English at home, even if their parents speak a different language.
However, language maintenance and revitalization efforts are also underway in many communities. For instance, some Native American tribes are working to revitalize their indigenous languages through language documentation, language education, and cultural programs. Similarly, some immigrant communities are establishing language schools and cultural centers to promote the use of their heritage languages.
Language Policy and Language Planning

Language policy and language planning are critical aspects of promoting linguistic diversity and language rights in the United States. At the federal level, the government has established several policies and programs to support language access and language education, including the Bilingual Education Act of 1968 and the Language Instruction for Newcomers to Canada (LINC) program.
Additionally, many states and local governments have their own language policies and programs, such as bilingual education programs, language access services, and cultural events. For example, the state of California has established a language access program to provide translation and interpretation services to limited English proficient (LEP) individuals.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the progress made in promoting linguistic diversity and language rights, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed. For instance, language barriers can limit access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities for LEP individuals. Moreover, language shift and language loss can result in the erosion of cultural heritage and community identity.
However, there are also opportunities for promoting linguistic diversity and language rights. For example, technology can be used to support language learning and language maintenance, such as through online language courses and language learning apps. Additionally, community-based language initiatives can help to promote language education and language preservation.
What is the most spoken language in the United States?
+English is the most spoken language in the United States, with over 239 million speakers.
How many languages are spoken in the United States?
+According to the United States Census Bureau, there are over 350 languages spoken in the United States.
What is language shift, and how does it occur?
+Language shift occurs when a community or individual shifts from speaking one language to another, often as a result of cultural, economic, or social factors. In the United States, language shift often occurs as immigrant communities become more assimilated into the dominant culture.
What are some strategies for promoting linguistic diversity and language rights?
+Some strategies for promoting linguistic diversity and language rights include language education programs, language access services, cultural events, and community-based language initiatives. Additionally, technology can be used to support language learning and language maintenance.
What are the benefits of promoting linguistic diversity and language rights?
+Promoting linguistic diversity and language rights can have several benefits, including fostering a more inclusive and equitable society, promoting cultural heritage and community identity, and supporting economic development and social mobility.
In conclusion, the United States is a linguistically diverse country with a rich cultural heritage. By promoting linguistic diversity and language rights, we can work towards creating a more just and vibrant cultural landscape. This requires a multifaceted approach that includes language education programs, language access services, cultural events, and community-based language initiatives. Additionally, technology can be used to support language learning and language maintenance. By recognizing and valuing the linguistic diversity of the United States, we can foster a more inclusive and equitable society that supports the well-being and prosperity of all individuals, regardless of their language background.



